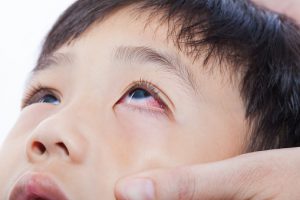
Pinkeye, also known as conjunctivitis, is one of the most common and highly treatable eye conditions. More than three million adults and children in the U.S. contract pinkeye every year.
Pinkeye occurs when the thin, clear tissue under the eyelid, known as the conjunctiva, becomes inflamed. This inflammation makes the blood vessels in the eye more visible, giving them a pink appearance. People who develop pinkeye typically experience pain, or feel a burning or itchy sensation. Their eyes may also tear and form a discharge that crusts while sleeping. Other symptoms may include swelling, tenderness or sensitivity to light.
There are several causes for pinkeye, but it is most commonly either viral, which is the most contagious form, or due to a bacterial infection. Other factors that can lead to pinkeye include exposure to irritants such as shampoo, cosmetics, dirt, or pool chlorine, an allergic reaction to pollen, dust, or smoke, or a reaction to eye drops or contact lenses. Usually a doctor can diagnose pinkeye through a routine examination.
Treating pinkeye depends on the cause of the condition. In most cases it is treated by administering artificial tears, which can be purchased over-the-counter, to treat the dryness and cold compresses to treat inflammation. If pinkeye has developed due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. Symptoms of pinkeye typically last anywhere from one to two weeks.
To avoid contracting pinkeye, take the following precautions:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and warm water. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer that contains at least 60 percent alcohol.
- Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes.
- Avoid sharing towels, blankets, and pillowcases.
- Do not share eye makeup, face makeup, makeup brushes, contact lenses or containers, or eyeglasses.
In rare cases pinkeye can lead to complications. Please see a doctor if you experience moderate to severe pain your eyes, if you have problems with your vision, or if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Pinkeye, also known as conjunctivitis, is one of the most common and highly treatable eye conditions. More than three million adults and children in the U.S. contract pinkeye every year.
Pinkeye occurs when the thin, clear tissue under the eyelid, known as the conjunctiva, becomes inflamed. This inflammation makes the blood vessels in the eye more visible, giving them a pink appearance. People who develop pinkeye typically experience pain, or feel a burning or itchy sensation. Their eyes may also tear and form a discharge that crusts while sleeping. Other symptoms may include swelling, tenderness or sensitivity to light.
There are several causes for pinkeye, but it is most commonly either viral, which is the most contagious form, or due to a bacterial infection. Other factors that can lead to pinkeye include exposure to irritants such as shampoo, cosmetics, dirt, or pool chlorine, an allergic reaction to pollen, dust, or smoke, or a reaction to eye drops or contact lenses. Usually a doctor can diagnose pinkeye through a routine examination.
Treating pinkeye depends on the cause of the condition. In most cases it is treated by administering artificial tears, which can be purchased over-the-counter, to treat the dryness and cold compresses to treat inflammation. If pinkeye has developed due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. Symptoms of pinkeye typically last anywhere from one to two weeks.
To avoid contracting pinkeye, take the following precautions:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and warm water. If soap and water are not available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer that contains at least 60 percent alcohol.
- Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes.
- Avoid sharing towels, blankets, and pillowcases.
- Do not share eye makeup, face makeup, makeup brushes, contact lenses or containers, or eyeglasses.
In rare cases pinkeye can lead to complications. Please see a doctor if you experience moderate to severe pain your eyes, if you have problems with your vision, or if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
To make an appointment at Flushing Hospital, please call 718-670-5486.
All content of this newsletter is intended for general information purposes only and is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult a medical professional before adopting any of the suggestions on this page. You must never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment based upon any content of this newsletter. PROMPTLY CONSULT YOUR PHYSICIAN OR CALL 911 IF YOU BELIEVE YOU HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY.
