Being admitted to a hospital or having to undergo a procedure can be a very stressful and even scary experience for many patients and their families, and that is especially true when that patient is a child.
In an effort to reduce the stress of our pediatric patients and offer a calming distraction for them, Flushing Hospital Medical Center is now offering children an escape from the hospital environment with the help of the Samsung Applied Virtual Reality headset. This state-of-the-art, interactive tool was purchased by Flushing Hospital thanks to a grant from the Child’s Play Foundation.
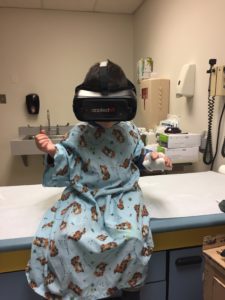 This fully mobile, virtual reality technology allows Flushing Hospital’s smallest patients to leave the confinement of their treatment area by taking them on a variety of exciting journeys. Pediatric patients can now relax on a sandy beach or tranquil ocean or they can visit any number of scenic destinations across the country and around the globe, including Los Angeles, Yellowstone National Park, London, Tibet, Iceland or Machu Picchu. The VR software is constantly being updated, offering patients an ever-expanding assortment of places to go to.
This fully mobile, virtual reality technology allows Flushing Hospital’s smallest patients to leave the confinement of their treatment area by taking them on a variety of exciting journeys. Pediatric patients can now relax on a sandy beach or tranquil ocean or they can visit any number of scenic destinations across the country and around the globe, including Los Angeles, Yellowstone National Park, London, Tibet, Iceland or Machu Picchu. The VR software is constantly being updated, offering patients an ever-expanding assortment of places to go to.
The headset is easy to operate and is being used to further assist Flushing Hospital’s Child Life Specialist while they care for patients. This technology offers an entertaining distraction to children when they are receiving important, yet typically anxiety-inducing treatments, such as blood draws, IV insertions, spinal taps, dressing changes and blood transfusions.
The virtual reality headset is utilized by most patients as it requires very little movement by the patient and it has proven to be very effective in helping children cope with stress associated with a clinical environment.
Patients as young as three years old have used the Samsung headsets and thus far, it has received an overwhelmingly positive response from both our patients and their parents. Both providers and family members have expressed that this technology has resulted in increased cooperation and enhanced comfort for our pediatric patients.
Flushing Hospital’s Pediatric Department is very grateful for this generous gift made possible by the Child’s Play Foundation and the staff is equally thrilled to have another tool to help them provide a positive atmosphere for our pediatric patients.
All content of this newsletter is intended for general information purposes only and is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult a medical professional before adopting any of the suggestions on this page. You must never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment based upon any content of this newsletter. PROMPTLY CONSULT YOUR PHYSICIAN OR CALL 911 IF YOU BELIEVE YOU HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY.




 Learning that your baby will be arriving early can be overwhelming. You may grow anxious as you wonder; what happens next? Having a premature baby does have its challenges; however you can better prepare yourself for what to expect through education.
Learning that your baby will be arriving early can be overwhelming. You may grow anxious as you wonder; what happens next? Having a premature baby does have its challenges; however you can better prepare yourself for what to expect through education.