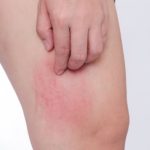
Urticaria (hives) is a skin condition caused usually by an allergic reaction or in some cases, unknown reasons. Hives can appear on any part of the body and appear when a substance within the body called histamine is released from cells called mast cells. This causes fluid to leak from blood vessels, causing a reaction on the surface of the skin.
Hives can be as small as a pencil point or appear as big welts and are usually red, itchy and have varying shapes. They usually last a few hours but can last a day or so, and if there is constant exposure to what is causing the condition, they will last much longer. The condition can be acute, lasting just a few weeks, to chronic which can go on for months.
The allergic reaction may be a result of exposure to certain allergens, chemicals in some food, insect bites, heat, cold and being out in sunlight. Certain medications can also be responsible for causing hives, most notably nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), aspirin, codeine, and morphine.
Hives usually resolve on their own in a few hours or days. One way to try to control the symptoms of hives is to avoid what is causing it, if it can be determined. Often times a physician will recommend taking an antihistamine. It is always suggested to see a physician if the condition becomes very uncomfortable or doesn’t resolve in a few days. If you would like to schedule an appointment with a physician at Flushing Hospital, please call 718-670-5486.
All content of this newsletter is intended for general information purposes only and is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Please consult a medical professional before adopting any of the suggestions on this page. You must never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking medical treatment based upon any content of this newsletter. PROMPTLY CONSULT YOUR PHYSICIAN OR CALL 911 IF YOU BELIEVE YOU HAVE A MEDICAL EMERGENCY.